Latest Newsletter Published
Catch up on the latest news from EuroGeographics, including the Open Maps For Europe 2 (OME2) project, our updated pan-European datasets, and news from our members.
Catch up on the latest news from EuroGeographics, including the Open Maps For Europe 2 (OME2) project, our updated pan-European datasets, and news from our members.

General Manager of the Surveying and Mapping Authority of the Republic of Slovenia, Tomaž Petek presents on EuroGeographics in his capacity as President of the Association.
The traditional meeting of Heads and employees of geodetic administrations in the Western Balkans region took place recently in Banja Luka.
Organised by the Administration for Geodetic and Real Estate Legal Affairs of the Republic of Srpska, the 16th Regional Conference on Cadastre and Infrastructure for Spatial Information also brought together representatives from donors, such as Kadaster Netherlands and the Swedish Agency for Cartography and Cadastre – Lantmateriet, and representatives from international associations, including EuroGeographics.
In addition to the hosts from Republic of Srpska, the conference was also attended by representatives of the geodetic administrations of Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina (Administration of the Federation of BiH), Serbia, Northern Macedonia and Montenegro.
Topics for discussion were divided into three areas: geospatial data infrastructure, cadastral and geodetic infrastructure; the real estate market; and sustainable development.
The 2024 event also paid special attention to the implementation of the Memorandum of Understanding and Cooperation in the field of cadastre, topographic research and cartography, geodetic networks and spatial data infrastructure, which was signed in 2019 in Neum. The Directors of cadastral and cartographic institutions discussed the possibilities of organising a regional project for building capacity.
General Manager of the Surveying and Mapping Authority of the Republic of Slovenia, Tomaž Petek presented the activities of EuroGeographics in his capacity as President of the Association. He also accepted a certificate of appreciation from the Administration for Geodetic and Real Estate Legal Affairs of the Republic of Srpska recognising its long-term collaboration and support in strengthening its capacities. Furthermore, the citation acknowledged that EuroGeographics efforts in promoting access to authoritative geospatial data have enhanced the Administration's activities and results, setting new standards in geospatial information management and land registration.
The conference concluded by recognising the importance of this type of cooperation in the region and the commitment for even more systematic and lasting integration in the region in the future in the form of working groups and joint projects.
The next regional conference will be held in Montenegro in 2025.
EuroGeographics has released updates for two pan-European datasets created using official data from its members, Europe’s National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registration Authorities.
The seamless administrative boundary and topographic datasets are created by the not-for-profit organisation using a unique data integration process which harmonises national data to standard specifications.
Users wanting to geo-reference statistical information will benefit from the latest version of EuroBoundaryMap (EBM 2024) which supports interoperability with applications based on European Union LAU and NUTS codes. It also includes the new NUTS regulation that came into effect on 1 January, as well as major updates from France, Germany, Great Britain, Greece, Spain, Slovenia, Switzerland and Lithuania. Licensing information for EBM 2024, which is widely used within the European Institutions through EuroGeographics agreement with Eurostat, can be found at https://eurogeographics.org/maps-for-europe/licensing/.
“EBM 2024 provides a complete update of our pan-European geo-database for administrative and statistical units to meet user requirements and is accessible as a full coverage dataset or national datasets,” said Victoria Persson, Project Manager – Data Access and Integration, EuroGeographics.
“It enables the exact matching of administrative areas in 56 European countries and territories using geospatial data from 39 EuroGeographics members. Available at 1:100 000 scale, it contains geometry, names and codes of administrative and statistical units."
Working with Germany’s Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy (BKG), which manages the production of both datasets, EuroGeographics has also updated its 1:250 000 scale dataset, EuroRegionalMap (ERM), which covers 51 European countries and territories, to ensure it continues to meet user needs.
Tim Trautmann, Product Manager for EBM and ERM from BKG explained: “ERM has a long history, starting in the early 2000s, and today contains around 7 million objects in 60 layers. It is now available under an open licence via Open Maps For Europe, and we’re seeing users discovering and embracing new ways to benefit from the data.”
“Our survey showed that its main use is as a reference dataset for base mapping with users stressing the need for complete and up-to-date information. To meet these requirements, ERM 2024 improves the settlement, administrative boundary and hydrographic themes, and we have enabled EuroGeographics members to provide data outside the thematic update cycle, which improves the timeliness.”
“This update also addresses several user feedback issues related to positional accuracy and edge matching. An additional validation algorithm for edge-matching has been implemented to improve the boundary harmonisation, and we have re-evaluated quality requirements to focus on those that are most important for the main use cases. This work is continuing.”
The Open Maps For Europe 2 (OME2) project is enhancing the five existing Open Maps For Europe datasets available via www.mapsforeurope.org. It is co-funded by the European Union and is being delivered by a consortium comprising: EuroGeographics; National Geographic Institute, Belgium; National Institute of Geographic and Forest Information, France; Hellenic Cadastre; General Directorate for the Cadastre, Spain; and Cadastre, Land Registry and Agency, The Netherlands.
EuroGeographics is an international not-for-profit organisation (AISBL/ IVZW under Belgian Law. BCE registration: 833 607 112) and the membership association for the European National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registry Authorities.
The OME2 project is co-funded by the European Union. It is being delivered by a consortium comprising: EuroGeographics, the not-for-profit membership association for Europe’s National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registration Authorities; National Geographic Institute, Belgium; National Institute of Geographic and Forest Information, France; Hellenic Cadastre; General Directorate for the Cadastre, Spain; and Cadastre, Land Registry and Agency, The Netherlands.
Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or European Commission. Neither the European Union nor the European Commission can be held responsible for them.
Open Maps For Europe was co-financed by the Connecting Europe Facility of the European Union and ended in 2022. It was coordinated by EuroGeographics, the voice of European National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registration Authorities, in partnership with the National Geographic Institute (NGI) Belgium.
The State Enterprise Centre of Registers, Lithuania, which processes main national data, has developed and launched an advanced solution for signing electronic documents and verifying identity in the electronic environment. The LT ID mobile application enables its users to sign documents in the electronic environment with an e-signature in a quick and easy way; the representatives of companies or organisations can seal documents with e-seal; whereas the residents who want to use digital services, are able to confirm their identity in the electronic environment with just a few clicks.
“Today, many people cannot even imagine their lives without a digital environment where they can quickly order goods or services from any place, remotely enter a business transaction or deal with questions of concern in state institutions without the necessity to visit them physically. All this is possible with a qualified electronic identification tool. The LT ID launched by the Centre of Registers is an advanced and effective solution that will help people and businesses to use digital services smoothly and reap their full benefits,” says Adrijus Jusas, Director General of the Centre of Registers.
“Lithuania is amongst the EU leaders in digitalisation of state services. 84% of the population and 94% of companies are using these services. The public sector takes the lead in developing competitive solutions, and the LT ID launched by the Centre of Registers is an excellent example of this. Therefore, we will continue to invest in this area. We should be not only the deployers of mature digital solutions, but also their developers,” says Aušrinė Armonaitė, the Minister of the Economy and Innovation.
The LT ID mobile app is designed to identify a person in the electronic environment and securely sign documents with a remote qualified electronic signature or seal them. The LT ID remote qualified electronic signature and seal are generated in the infrastructure managed by the Centre of Registers, which complies with the EU requirements for the creation of qualified signatures and seals; therefore, this solution is not only simple but also secure and reliable one.
The LT ID - a reliable key to unlock the digital world
The LT ID e-signature can be used by all citizens of the Republic of Lithuania or persons who have a residence permit in Lithuania and are at least 14 years old. The LT ID seal is intended for the use of legal entities registered in Lithuania, i.e. companies, institutions, organisations, and the right to use an e-seal is granted to the head of a legal entity or a person authorised by them.
The LT ID is recognised as an EU-compliant tool for the creation of qualified electronic signatures and seals, as concluded by the Deutsche Telekom Security, a German company that has conducted an international audit. The distribution of qualified electronic signature and seal certificates in the LT ID mobile app has been authorised by the Communications Regulatory Authority of the Republic of Lithuania. E-signature and seal certificates as well as electronic documents signed using the LT ID are recognised in all EU countries. The e-signature certificate issued by the LT ID can be used for reliable identification of a person in the electronic environment both in Lithuania and across the EU.
Benefits and operating principle
The LT ID is an e-signature of a natural person and/or e-seal of a legal entity in one mobile application. Thus, e.g., a company manager can not only sign electronic documents on their smart device with a single application, but also electronically seal their documents on behalf of the company, as well as confirm their identity in the electronic environment and use electronic services as a natural person.
Currently, the LT ID can be used for signing electronic documents in the GoSign signing platform, for logging in and performing actions in the Self Service of the Centre of Registers and other systems of the Centre of Registers. Soon, this tool will be available for using electronic services in the E-Government Gateway as well as in the electronic document signing platform Mark Sign. In future, the list of service providers is planned to expand and include the most relevant electronic service providers for the residents and businesses.
The operating principle of the LT ID is rather simple: when the holders of e-signature or e-seal certificate initiate the signing process in the electronic environment, a notification pops up in the mobile application asking to enter the created PIN code. Then, the documents are signed with e-signature or sealed with e-seal.
How to become a user?
Becoming a LT ID user is very easy - you just need to download a free mobile application from one of the mobile application stores (Google Play or App Store) and create the desired e-signature or e-seal certificate by following the wizard in the app. The LT ID users only need to have a mobile device with an Internet connection; no additional devices for creating an e-signature (USB, smart or SIM cards) are required.
To create the LT ID e-signature or e-seal remotely, the mobile app user must have one of the following qualified means of identity verification: a mobile e-signature, a qualified e-signature stored on the USB device or a smartcard.
Those who do not have any of the above means can become the LT ID users by visiting the nearest Customer Service Unit of the Centre of Registers, where specialists will confirm the identity of the customer, help them install the LT ID application and enjoy its benefits.
The LT ID electronic signature and seal certificates are issued for 5 years.
More information on the benefits and possibilities of the LT ID is available at www.ltid.lt.
Our latest newsletter focuses on the Open Maps For Europe 2 (OME2) project, and in particular the first release of a prototype for harmonised large-scale, high-value data. It also calls for feedback on version one which provides 1: 10 000 scale authoritative administrative boundary and transport data for Belgium, France and The Netherlands.
Read and subscribe to the newsletter.
The OME2 project is co-funded by the European Union. It is being delivered by a consortium comprising: EuroGeographics; National Geographic Institute, Belgium; National Institute of Geographic and Forest Information, France; Hellenic Cadastre; General Directorate for the Cadastre, Spain; and Cadastre, Land Registry and Mapping Agency, The Netherlands.
Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or European Commission. Neither the European Union nor the European Commission can be held responsible for them.
The Open Maps For Europe 2 (OME2) project has today (28 May 2024) announced the first release of a prototype for harmonised large-scale, high-value data.
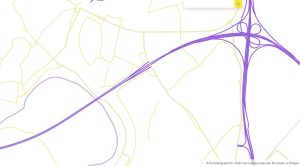
OME2 Prototype Maastricht border.
Available via www.mapsforeurope.org, version one provides 1: 10 000 scale authoritative administrative boundary and transport data for Belgium, France and The Netherlands. It is the first dataset created using the new production process, developed by several OME2 Consortium members led by National Institute of Geographic and Forest Information (IGN France), to deliver edge-matched official geospatial information from multiple national sources. The image right shows the Maastricht border.
In addition to IGN France, the project partners comprise: EuroGeographics, the not-for-profit association for Europe’s National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registration Authorities; National Geographic Institute, Belgium; Hellenic Cadastre; General Directorate for the Cadastre, Spain; and Cadastre, Land Registry and Mapping Agency, The Netherlands. Images below show: La Defense, Paris; Brussels; and Amsterdam.
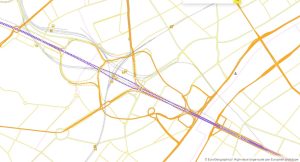
OME2 Prototype La Defense, Paris.
“This is a really exciting milestone that will benefit national providers of geospatial data and users alike,” said Victoria Persson, Project Manager – Data Access and Integration, EuroGeographics.
“The prototype is aligned to key EU policies, as well as UN core geospatial data recommendations for local level actions, and provides large-scale administrative boundary information as well as transport and railway networks, ports and airports.”
“The authoritative data is harmonised across countries and available via the Open Maps For Europe interface. This saves users time, effort and resources as they will no longer need to visit individual Member State geoportals to access specific datasets, spend significant resources connecting them, or agree to multiple licences.”
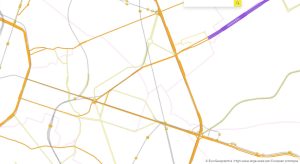
OME2 Prototype Brussels.
She continued: “Our members are recognised as important enablers of cross-border data applications and services. By automating the production process, OME2 now transforms their national data to meet the specifications for high-value pan-European datasets. Members simply complete a conversion table which typically takes just a few days, significantly reducing the time and resources required. Additional work is then only needed in the rare event that the data structure changes. The process also responds to user needs by enabling annual updates.”
“Our members can re-use these techniques nationally and exchange good practices to advance the data sharing tools needed to deliver free-flowing, interoperable data for the single market. In doing so, OME2 demonstrates how demand for geospatial information in all common data spaces of the European Strategy for Data can be met.”
By the end of 2025, the OME2 prototype is expected to cover 10 countries with three key themes identified by users and defined as high value by the European Commission – administrative boundaries, transport and hydrography. The project, which is co-funded by the European Union, is also enhancing the five existing Open Maps For Europe datasets, including the pilot Open Cadastral Map.
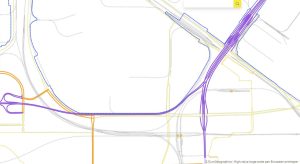
OME2 Prototype Amsterdam.
EuroGeographics is an international not-for-profit organisation (AISBL/ IVZW under Belgian Law. BCE registration: 833 607 112) and the membership association for the European National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registry Authorities.
The OME2 project is co-funded by the European Union. It is being delivered by a consortium comprising: EuroGeographics, the not-for-profit membership association for Europe’s National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registration Authorities; National Geographic Institute, Belgium; National Institute of Geographic and Forest Information, France; Hellenic Cadastre; General Directorate for the Cadastre, Spain; and Cadastre, Land Registry and Mapping Agency, The Netherlands.
Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or European Commission. Neither the European Union nor the European Commission can be held responsible for them.


Sallie Payne Snell, Secretary General and Executive Director, EuroGeographics, and Prof. Dr. Paul Becker, President BKG Germany, sign production management agreement for pan-European datasets.
Germany’s Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy (BKG) will continue to manage production of pan-European datasets after signing a new agreement with EuroGeographics.
As a result, BKG is responsible for three open datasets available via the Open Maps For Europe (OME) user interface, as well as a database of administrative boundaries and 1:250 000 topographic data. The datasets are created using authoritative national geospatial and land information from members of EuroGeographics, the not-for-profit membership association for Europe’s National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registration Authorities.
In addition, the National Institute of Geographic and Forest Information (IGN France) continues to manage the production of EuroGlobalMap, 1: 1 million scale multi-themed topographic open data also delivered through the OME portal.
Sallie Payne Snell, Secretary General and Executive Director, EuroGeographics, said: “BKG’s expertise is integral to our unique data integration process. In addition to harmonising national geospatial information to standard specifications, it has a wealth of experience in deriving information from master databases.”
“We are delighted to continue our well-established partnership with them to provide authoritative and trusted pan-European data for making critical decisions about people and places.”
Prof. Dr. Paul Becker, President BKG Germany, said: “We are pleased to continue to make an essential contribution to the provision of harmonised, cross-border geospatial data on behalf of EuroGeographics. The requirements of users – above all the European Commission – inspires us to produce even more demand-orientated data for Europe.”
Under the agreement BKG manages the technical, quality and documentation for five datasets:
Open datasets available through www.mapsforeurope.org
BKG also provides the OME pan-European Imagery service, a processed mosaic with a 10 metre resolution, created from European Union´s Earth observation programme Copernicus (Sentinel-2, L1C-L2A). It can be used as a reference for mapping and visualisation.
EuroGeographics is an international not-for-profit organisation (AISBL/ IVZW under Belgian Law. BCE registration: 833 607 112) and the membership association for the European National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registry Authorities.
The OME2 project, which builds on the success of Open Maps For Europe, is co-funded by the European Union. It is being delivered by a consortium comprising: EuroGeographics, the not-for-profit membership association for Europe’s National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registration Authorities; National Geographic Institute, Belgium; National Institute of Geographic and Forest Information, France; Hellenic Cadastre; General Directorate for the Cadastre, Spain; and Cadastre, Land Registry and Mapping Agency, The Netherlands.
Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or European Commission. Neither the European Union nor the European Commission can be held responsible for them.
Open Maps For Europe ended in 2022. It was co-financed by the Connecting Europe Facility of the European Union.
EuroGeographics is recruiting a part-time Administrative Officer.
The successful applicant will provide support to the team running the international non-profit membership association, facilitate the smooth running of the office and undertake accountancy duties.
Deadline for applications is 31 May 2024.
Only shortlisted candidates will be contacted for an interview. CV and personal data of non-selected candidates are not shared with anyone outside EuroGeographics, unless specifically authorised by the applicant.
Shadow Day at the State Land Service of Latvia gives school pupils an insight into the day-to-day activities of a geospatial professional, reports Rasa Bērzina, Strategic Planning Expert.
 Organised by the Latvian subsidiary of Junior Achievement, the annual careers event connects employers and young people to help them make choices about their future professions and prepare for the labor market. For employers, it is a good opportunity to raise their company's profile and attract future colleagues.
Organised by the Latvian subsidiary of Junior Achievement, the annual careers event connects employers and young people to help them make choices about their future professions and prepare for the labor market. For employers, it is a good opportunity to raise their company's profile and attract future colleagues.
In April 2024, 24 curious students from various educational visited the State Land Service to find out more about its activities and gain an insight into its everyday work. Applications were received from students who wanted to shadow the Director General, Public Relations specialist, Archivists, Customer Service specialists, as well as Building Cadastral Surveying specialists and Cadastre Development managers. The youngest participant was a 2nd grade student interested in the archivist profession, but there were also many students who will graduate from high school this summer and are eager to choose their field of study.
Rasa Bē rzina explained: “The shadows were mostly concentrated in our Riga Coworking spaces, some of them being in our Jelgava office as well. We organised the first part of the event as getting to know each other by playing the ‘association game’ together. The Director General and the Cadastre Development manager gave the students a general introduction to the areas of activity of the State Land Service. An interesting story with practical demonstrations of various archive documents was given by the Head of our Archives. Students had a chance to learn how to use various tools to carry out building measurements also. In addition, we played a short quiz and took a walk together to get to know the co-working office premises, so that afterwards the students could get to know their chosen professions more closely.”
rzina explained: “The shadows were mostly concentrated in our Riga Coworking spaces, some of them being in our Jelgava office as well. We organised the first part of the event as getting to know each other by playing the ‘association game’ together. The Director General and the Cadastre Development manager gave the students a general introduction to the areas of activity of the State Land Service. An interesting story with practical demonstrations of various archive documents was given by the Head of our Archives. Students had a chance to learn how to use various tools to carry out building measurements also. In addition, we played a short quiz and took a walk together to get to know the co-working office premises, so that afterwards the students could get to know their chosen professions more closely.”
“Our colleagues had prepared various tasks for the students - the shadows of the Public Relations specialist, for example, created a joint photo collage; the shadows of the Cadastre Development manager had a lot of questions about various topics related to maps, Cadastre and various buildings; and future archivists had the opportunity to walk around the spacious premises of our Archive and familiarise themselves with various documents of one of the most notable buildings of Riga.”
“We are thankful to all the curious shadows who spent Shadow Day at the State Land Service! We are happy to have such knowledgeable, purposeful, attractive and communicative students! Our future is in good hands.”
GreenData4All’s plans to update rules for environmental spatial data are an opportunity to better govern and access geospatial information within the European Union (EU), says EuroGeographics.
The not-for-profit association for Europe’s National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registration Authorities (NMCAs) welcomed modernisation of INSPIRE Directive rules but warned that removing location data from its scope risks having little or no governance in the geospatial sector. It added that the GreenData4All initiative should include a separate chapter for geospatial data and its role in the Green Deal data space, noting that inclusion of NMCAs is vital for overcoming shortcomings in existing governance.
Marjana Zelic, Senior Research and Policy Officer, EuroGeographics said: “Revision of the INSPIRE Directive represents an important milestone for EuroGeographics’ members, many of whom have invested significant resources in its implementation to ensure their data is discoverable, accessible and interoperable. Whilst we support any action to simplify the technical provisions, such as data harmonisation and network services, previous investments must be protected and solutions identified to finance new ones.”
“Information about location is a critical component for environmental monitoring and reporting providing an accurate continuous observation of the territory, which is necessary for the Green Deal. While INSPIRE is rigid, it provides a clear framework for managing geospatial data and at least half of the 34 cross-sectoral categories within its existing thematic scope are from the geospatial sector. Indeed, the Implementing Act on High-Value Datasets (HVD) refers to the INSPIRE rules to make listed geospatial data available and accessible for reuse, and as the official national providers of map, cadastral and land registration information, our members appreciate this level of coherence.”
“Without defining which other sectoral tools would cover non-environmental data if it is removed from the scope of INSPIRE, there is a risk of having little or no governance in the geospatial sector. Currently there is no dependable policy framework or ‘home’ for geospatial within the EU, with the management of the sector fragmented across various directives including Open Data and PSI Reuse and the Implementing Act on HVD, as well as INSPIRE.”
“As a continuation of 15 years of investment in the implementation of INSPIRE, EuroGeographics’ members are keen to make their data available for the future Green Deal data space which they consider a priority. This is therefore an opportunity to develop an appropriate solution to better govern both geospatial data and the geospatial knowledge infrastructure. These support not only Green Deal priority actions on climate change, circular economy, zero pollution, biodiversity, and deforestation, but every single data space in the European Strategy for Data.”
Read EuroGeographics full feedback on the Greendata4All call for evidence.
EuroGeographics is an international not-for-profit organisation (AISBL/ IVZW under Belgian Law. BCE registration: 833 607 112) and the membership association for the European National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registry Authorities.
EuroGeographics is registered on the EU Transparency Register and bound by its code of conduct: TR 51080067776-74